

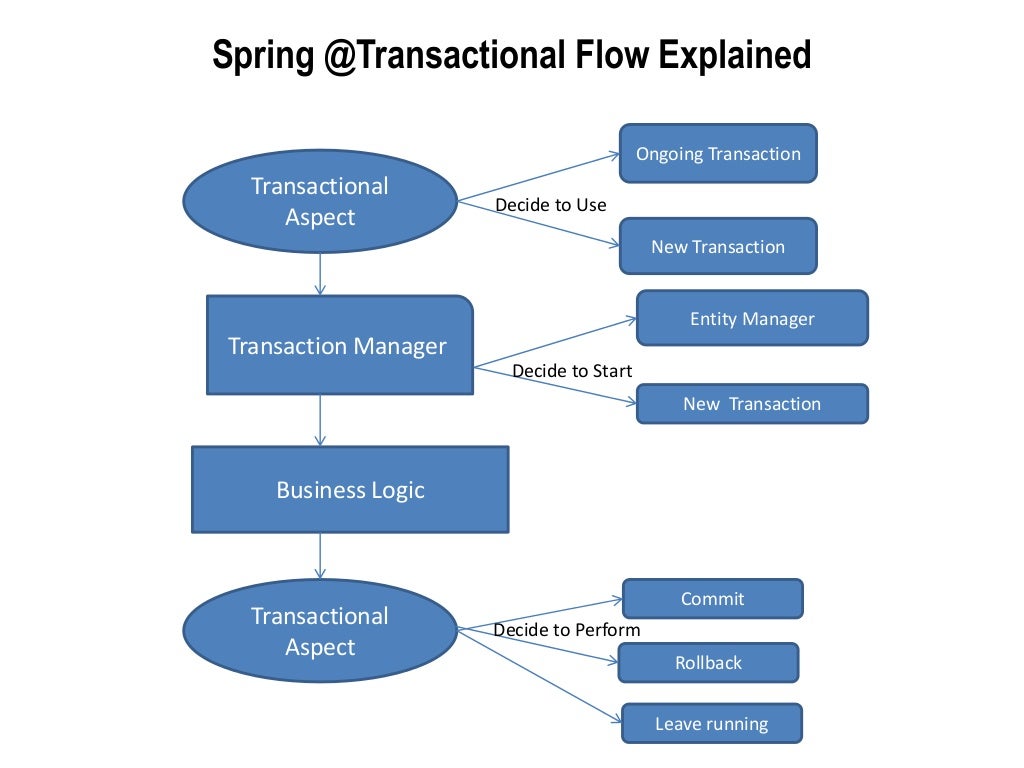
In this case, you cannot rely on the transaction manager built into the resource itself. Global transaction managers:Ī global transaction manager is a transaction manager that can coordinate transactions over multiple resources. Local transactions are easier to be implemented. Local transaction management can be useful in a centralized computing environment where application components and resources are located at a single site, and transaction management only involves a local data manager running on a single machine. In this case, the implementation of the transaction manager is typically embedded in the resource itself and the Spring transaction manager is just a thin wrapper around this built-in transaction manager. Local transaction managers:Ī local transaction manager is a transaction manager that can coordinate transactions over a single resource only. EJBs requires an application server, but Spring transaction management can be implemented without a need of application server. Spring supports both programmatic and declarative transaction management. The Spring’s transaction support aims to provide an alternative to EJB transactions by adding transaction capabilities to POJOs. Spring framework provides an abstract layer on top of different underlying transaction management APIs. Commit the transaction (updates become visible if the transaction is successful).Execute several queries (although any updates to the database aren’t actually visible to the outside world yet).

Durability: Once a transaction has completed, the results of this transaction have to be made permanent and cannot be erased from the database due to system failure.Ī simple transaction is usually issued to the database system in a language like SQL in this form:.Isolation: There may be many transactions processing with the same data set at the same time, each transaction should be isolated from others to prevent data corruption.Consistency: This represents the consistency of the referential integrity of the database, unique primary keys in tables etc.Atomicity: A transaction should be treated as a single unit of operation which means either the entire sequence of operations is successful or unsuccessful.The concept of transactions can be described with following four key properties described as ACID: Transaction management is an important part of and RDBMS oriented enterprise applications to ensure data integrity and consistency. These actions should either complete entirely or take no effect at all. It is critical in any form of applications that will interact with the database.Ī database transaction is a sequence of actions that are treated as a single unit of work.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
